While KDirStat is a KDE program, it runs fine on every X11 desktop, i.e., it runs on Linux, BSD, and lots of other Unix-type systems (Solaris, HP-UX, AIX, ...).
MS Windows Users please note that there are operating systems and window systems beyond those from Redmond, WA. This may come as a surprise to some people. ;-) There is a MS Windows clone called WinDirStat. Yes, that one is the clone. KDirStat is the original.
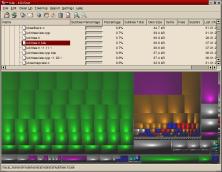
Display Features
- Graphical and numeric display of used disk space
- Files kept apart from directories in separate items to prevent cluttering the display
- All numbers displayed human readable - e.g., 34.4 MB instead of 36116381 Bytes
- Different colors in the directory tree display to keep the different tree levels visually apart
- Display of latest change time within an entire directory tree - you can easily see what object was changed last and when.
Treemap Display
- Treemap as alternate (auxiliary) view of a directory tree
- Easily find large in a directory tree: You see the entire tree at once. Large rectangles are large files - you can see them even if they are hidden somewhere deep within the tree.
- Treemap view slaved to the tree (list) view: Click on a file in the treemap, and it is selected in the tree view - and vice versa.
- Treemap tiles are colored by file type - all images in cyan, all audio tracks (MP3 etc.) in yellow, executables in magenta etc.; you can see from the color what a treemap rectangle is.
- Many treemap variants available:
o Plain treemap
o Squarified treemap (no thin elongated rectangles)
o Cushion treemap
o Colored treemap
o All combinations of the above - Fast implementation: Treemap built in fractions of a second (on quite ordinary machines: Athlon-550 class)
- Treemap subwindow can be resized as the user prefers
- Treemap can be switched off with a single keypress (F9)
- Context menu with cleanup actions etc.
- Zoom the treemap in/out treemap with double click (left/right)
- Many treemap configuration options
Directory Reading
- Stays on one file system by default - reads mounted file systems only on request. You don't care about a mounted /usr file system if the root file system is full and you need to find out why in a hurry, nor do you want to scan everybody's home directory on the NFS server when your local disk is full.
- Network transparency: Scan FTP or Samba directories - or whatever else protocols KDE support.
- Cache file reading and writing: Use the supplied Perl script kdirstat-cache-writer to scan directory trees in cron jobs over night and view the result with KDirStat whenever it is convenient - without creating I/O load on the machine you are scanning. You can also use that script to scan directories on a server and view the result on any machine that has KDE running. The server doesn't need any more infrastructure than a normal Perl installation (i.e., no X11 or KDE required).
- PacMan animation while directories are being read. OK, this is not exactly essential, but it's fun.
Cleaning up
- Predefined cleanup actions: Easily delete a file or a directory tree, move it to the KDE trash bin, compress it to a .tar.bz2 archive or simply open a shell or a Konqueror window there.
- User-defined cleanup actions: Add your own cleanup commands or edit the existing ones.
- "Send mail to owner" report facility: Send a mail requesting the owner of a large directory tree to please clean up unused files.



